What Is .NET Aspire Orchestration? A Complete Guide for Developers
If you’ve ever worked on a distributed application; with APIs, databases, caches, and background workers, you know the pain of wiring everything together locally.
.NET Aspire orchestration is here to make that process simple, fast, and developer-friendly.
In this article, you’ll learn:
- What orchestration in .NET Aspire means
- Why it matters for modern application development
- How it works with real-world examples
- Where to learn more
What Is .NET Aspire?
.NET Aspire is a Microsoft framework that makes building cloud-native and distributed applications easier.
One of its most powerful features is orchestration, ability to define and run multiple services (APIs, databases, caches, etc.) together with minimal setup.
Think of orchestration as your application’s central conductor, making sure every service starts on time, knows where to find others, and works in harmony.
What Does Aspire Orchestration Do?
In simple terms, orchestration in .NET Aspire lets you:
- Define your entire app stack in C# (instead of YAML or bash scripts)
- Launch all components, projects, containers, and cloud resources—with one command
- Handle dependencies so services start in the right order
- Inject configs like connection strings automatically
- Monitor everything with a built-in dashboard
How It Works (Step-by-Step)
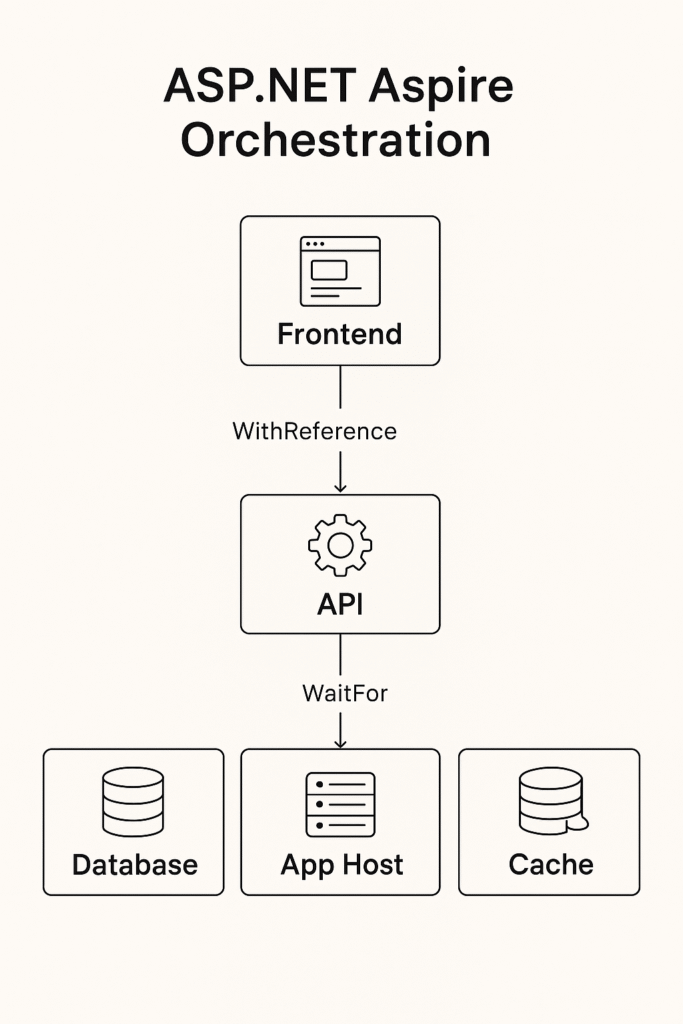
- App Host Project
You create a special.AppHostproject where you declare all your resources, APIs, frontends, databases, message queues, etc. - Service Registration
You register each component usingbuilder.Add...()methods. - Dependency Setup
You specify how services depend on each other using.WithReference()and.WaitFor(). - Run & Monitor
Aspire spins up everything—your local projects and required containers—and you can track them via its dashboard.
Real-World Analogy
Imagine running an online shop locally:
- Frontend (customer UI)
- Backend API
- Database
- Cache (Redis)
- Background worker
Instead of starting each manually, wiring configs, and remembering start-up order, you define it once:
var builder = DistributedApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
var cache = builder.AddRedis("cache");
var api = builder.AddProject<Projects.ApiService>("api")
.WithReference(cache)
.WaitFor(cache);
var frontend = builder.AddProject<Projects.Frontend>("frontend")
.WithReference(api)
.WaitFor(api);
builder.Build().Run();
Hit Run, and Aspire:
- Starts the cache container
- Launches the API once cache is ready
- Launches the frontend after the API is running
- Configures connection strings automatically
- Displays logs, health, and telemetry in a dashboard
Why Use Aspire Orchestration?
- Zero “works on my machine” headaches: Every developer runs the same local stack.
- Faster onboarding: New team members can start coding within minutes.
- Reduced complexity: No need for manual Docker Compose or Kubernetes YAML during development.
- Better visibility: Built-in telemetry and health checks.
Aspire vs. Production Orchestration
Important: Aspire orchestration is for local development.
In production, you’d still use Kubernetes, Azure Container Apps, AWS ECS, or similar tools.
Think of Aspire orchestration as:
- Development productivity booster
- Local environment standardizer
- Onboarding accelerator
Key Benefits at a Glance
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Code-first configuration | No separate YAML files to maintain |
| Dependency management | Services start in the right order |
| Built-in observability | Logs, metrics, and health checks in one place |
| Seamless container support | Works with Docker automatically |
| Fast onboarding | New devs can run the full stack instantly |